New to 2D animation? Here’s what actually happens behind the scenes. The real process, not the romanticised version. Let’s see what is 2D animation?
At its core, 2D animation is straightforward. It’s about creating the illusion of movement by showing a series of slightly different images in quick succession. Yet it’s a skill that combines art with technical know-how, and it’s been central to entertainment for generations.
We’ve put together this guide to walk you through how it works, the distinction between classic and modern approaches, and what the career prospects actually look like.
2D animation – definition and history
When you think about 2D animation, you’re looking at an art form that’s all about creating the illusion of motion in a flat, two-dimensional space. It covers everything from characters and creatures to visual effects and backgrounds. The principle is surprisingly straightforward. Take a series of individual drawings, show them one after another at the right speed, and your brain automatically stitches them together into smooth, continuous movement.

The story of 2D animation goes back to the late 1800s. Artists like Émile Reynaud and J. Stuart Blackton figured out something remarkable that, if you put sequential images together, you could fool the eye into seeing motion. They experimented, discovered the underlying principles, and essentially opened the door for everyone who came after them. The techniques they pioneered became the foundation for an entire medium.

Now, the medium itself has evolved quite a bit. In the beginning, animation meant sitting down and drawing every single frame by hand, and if you’ve ever tried that, you know it’s exhausting work😆. But technology has changed the game.
Modern animators have access to powerful software like Toon Boom Harmony and Adobe After Effects, tools that make the process faster and more efficient. That said, despite all these digital tools, the medium hasn’t lost its artistic soul. It’s still recognisably 2D animation, with all the distinctive visual quality that comes with it.
History of animated films – origins and evolution
Back when 2D animation first started, it was genuinely gruelling work. Animators had to hand-draw every single frame, and to give you a sense of scale:
One second of finished animation typically required 24 individual drawings.
Now, not every animator used all 24 frames per second. It depended on the style and budget of the project.
- Some went for the full 24 unique drawings per second (24fps) to get the smoothest possible motion.
- Others worked more economically, creating just two drawings per frame cycle, which translates to 12fps.
This approach, called “on 2s”, became pretty standard in the industry because it cut down significantly on both production time and costs without sacrificing too much visual quality.
That traditional way of doing things has transformed dramatically over the years. When digital tools arrived (software like Toon Boom Harmony and Adobe After Effects) the possibilities exploded. Animators could suddenly create far more intricate animations with richer visual detail.
You can see this evolution everywhere, from the way Walt Disney pioneered the craft with “Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs” to the sophisticated digital animations you see online today. The medium has spread across film, television, streaming platforms, and everywhere else, constantly finding new ways to tell stories.
Nostalgia and timeless appeal
There’s something special about 2D animation that crosses generational lines….
People of all ages feel a genuine connection to it, and there’s a familiarity to the medium that just feels right, something comforting about hand-drawn animation that digital techniques haven’t entirely replaced.
What makes 2D animation so enduring is its flexibility. It works across virtually every genre you can think of, and it’s genuinely accessible. If you’re thinking about getting into animation yourself, 2D is often where people start. Despite all the technological progress we’ve seen, 2D animation hasn’t lost its appeal. There’s something emotionally direct about it that resonates with viewers, whether it feels nostalgic or fresh.
2D animation today
If you look around the internet right now, 2D animation is everywhere and it’s thriving. You’ll find it in TV shows, video games, feature films, commercials, mobile apps, and websites. Companies are using it constantly to grab attention and tell their stories.
Take a look at what studios like Explain Visually are doing with projects for brands like Mitsubishi Electric, or how indie games like “Cuphead” have become cult classics thanks to their hand-drawn style. Even social media platforms like Snapchat are investing in short animated episodes because they know audiences eat that stuff up.
You probably see 2D animation every single day without even realising it. Ads, entertainment content, educational videos. Animations play a massive role in how we experience the internet.
Television animation has exploded, and streaming services are constantly hunting for fresh content. The demand for skilled 2D animators has grown massively over the past decade, and it shows no signs of slowing down.
Companies across industries, from marketing to education to pure entertainment, are looking for artists who can create original, engaging animations that actually capture people’s attention and deliver messages effectively.
Visit Explain Visually to learn how we help brands make their mark on the world with 2D animation.
Read also: Animation vs. Illustration: Which is More Effective [Based on Research]
Styles and techniques in 2D animation
Traditional animation

Traditional animation (sometimes called hand-drawn or classical animation)is a time-honored animation techniquein the business. The principle is straightforward:
you draw each individual frame by hand to create the appearance of movement.
Typically, animators would sketch each frame on paper first, then trace it onto transparent sheets called cels. These cels get layered over static background artwork to form the complete scene.
Every frame shows a tiny shift in position or expression. When you play these frames back in sequence, the eye perceives smooth, continuous motion. It’s labour-intensive work that demands serious skill and patience. To give you a sense of scale, a single animated feature can require thousands upon thousands of hand-drawn frames.
Modern animation
Modern 2D animation takes a completely different approach compared to the traditional methods. Instead of drawing everything by hand, animators use computers to speed up and simplify the entire process.
- Adobe Animate,
- Toon Boom Harmony,
- After Effects.
These programs come packed with features (vector-based drawing tools, rigging systems, motion tweening) that cut down on the repetitive work of drawing frame after frame.
What’s particularly interesting about modern animation is how it connects with other digital technologies. You can create interactive animations for video games, mobile apps, websites… Pretty much anywhere.
Here’s something worth noting!
Modern software can actually mimic traditional animation styles. Artists can produce work that looks and feels hand-drawn whilst still taking advantage of all the efficiency that digital tools offer.
Read more: Animated ads – types, examples, prices.
What is the difference between 2D and 3D animation?
When you compare 2D and 3D animation, you’re looking at two completely separate techniques. They differ in their visual appearance, the way they’re produced, and the contexts where each one works best.

Visual style
2D animation works within two dimensions. Basically, just width and height. The result is a flat visual style that tends to lean towards stylised, cartoonish aesthetics. Animators create characters and objects by drawing them frame by frame, either by hand or using computer software.

3D animation takes things a step further by introducing a third dimension: DEPTH. Instead of just working with horizontal and vertical movement, animators also account for how close or far something appears. This added dimension gives animations a much more realistic, tangible quality.
Production process
2D Animation involves drawing each frame individually, which can be less complex and quicker to produce.
Creating 3D animation involves building three-dimensional models and setting them up for movement through a process called rigging.
- This requires more sophisticated software: programs like Blender or Autodesk Maya.
- It also demands a solid grasp of 3D modelling, texturing, and lighting techniques.
The whole workflow is considerably more complex and labour-intensive than 2D, which is why it typically involves teams of specialists rather than individual artists.
Cost and time
In most cases, 2D animation is cheaper and quicker to create than 3D. It doesn’t need the same sophisticated equipment or technical infrastructure.

3D animation usually comes with a higher price tag and longer production timelines because the process is inherently more complex. It needs powerful computers and specialist software. It’s therefore evident that this drives costs up considerably.
Read more: Price of an explainer video – how much does it cost and why?
The animation process
Let’s look at how 2D animation production actually works. It’s worth pointing out that every animated film gets made differently. Studios use various techniques and technologies depending on the project.
There’s no single “correct” way to animate!
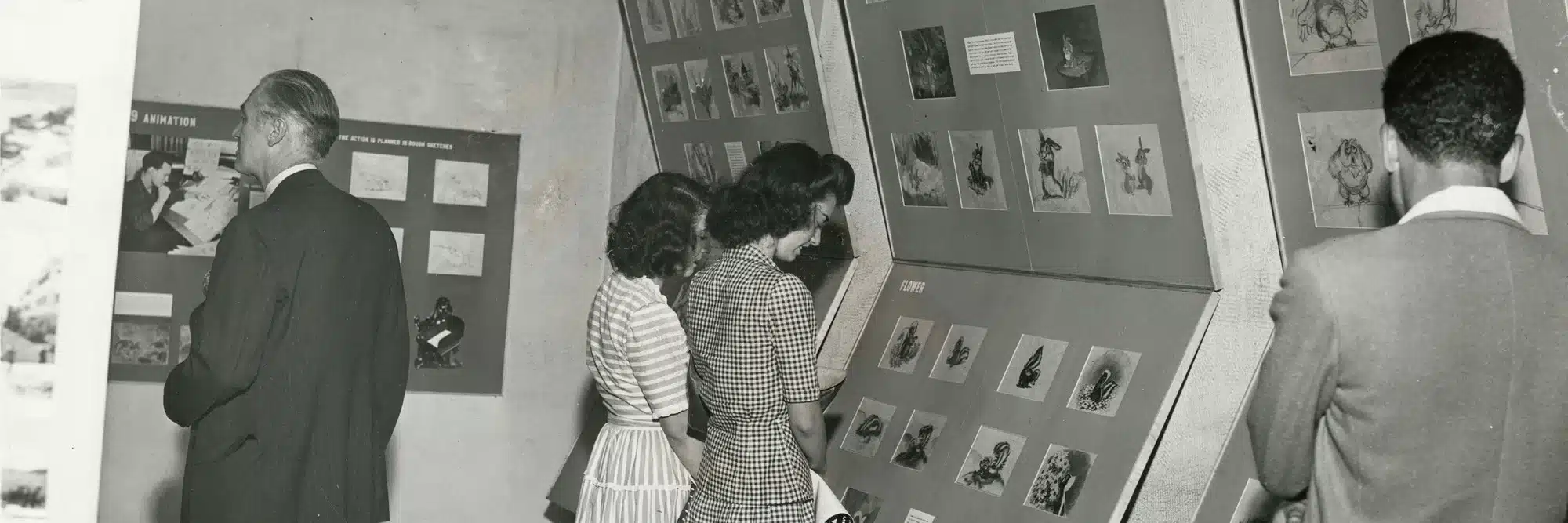
The steps we’re about to describe might happen in a different order depending on who’s doing the work. What you’ll see here is a commonly used approach that major animation studios like Disney, Dreamworks, and Ghibli tend to follow.
The animation process from 1938 @ Copyright by Disney
Creating 2D animation breaks down into three main phases:
- pre-production;
- production;
- post-production.
1. Pre-production stage
The pre-production phase involves sourcing inspiration, shaping the core idea, completing the script, and organising the production timeline.
It’s built from a series of smaller stages, all of which form the foundation for the complete animated project.
2. Production stage
The production stage involves designing the visuals and, depending on the project, may also include:
- composing theme songs,
- storyboarding,
- developing concept art,
- recording voices,
- animating,
- applying ink and color.

Each of these processes contains several sub-stages, which are crucial to constructing a complete animated piece.
3. Post-production stage
Post-production is where sound design and editing come together to polish the finished animation.
- Sound design and effects.
- Recording and editing dialogue.
- Sound mixing and final assembly.
- Visual effects integration.

Post-production is where everything comes together. All the separate pieces of the animation (visuals, sound, effects) get assembled into a polished, cohesive final product. This stage demands tight collaboration between sound designers, editors, and directors to make sure the audio and visuals work seamlessly and deliver the creative vision the team set out to achieve.
Artistic and technical skillsevery 2D animator should have
- To work in 2D animation, you need a strong grounding in drawing and illustration. These skills are the foundation for designing expressive characters and building scenes that feel dynamic.
- Understanding animation fundamentals (timing, spacing, squash and stretch), is equally important. These principles are what make movement look natural and characters feel alive.
- Technically, you’ll need to be comfortable with industry-standard software like Adobe Animate or Toon Boom Harmony to produce animations quickly and professionally.
- Attention to detail and a good sense of composition are also crucial. They help animators create scenes that are both visually striking and narratively clear.
If you’ve got experience with storyboarding or character design, that’s even better! It means you can contribute more meaningfully to the creative process and ensure the animation supports the project’s overall vision.
Job prospects and pay in 2D animation
If you’re looking at a career in 2D animation, the good news is there’s work across multiple industries: feature films, TV shows, video games, advertising…. Within these sectors, animators typically work for animation studios, production houses or ad agencies, creating everything from commercials to content for mobile apps and websites.
The job titles vary quite a bit. You might work as an animator, storyboard artist, character designer, or background painter, among other roles. As technology keeps advancing, new positions keep popping up, which means more opportunities for people breaking into the field.
Salary ranges and growth prospects
Salaries for 2D animators depend quite a bit on experience, location, and which industry you’re working in. Generally, entry-level positions pay significantly less than mid-level roles, which in turn earn less than senior positions.
What animators actually earn and career growth?
In the United States, entry-level positions typically offer around USD $45,000-$50,000 per year, whilst mid-level roles average USD $60,000-$75,000. Senior positions and specialists can earn USD $80,000-$100,000+. [1]
In Canada, beginners can expect between CAD $46,000 and $58,000, with mid-level roles ranging from CAD $53,000 to $70,000. [2]
In Australia, entry salaries start around AUD $44,000-$50,000, whilst mid-level positions command between AUD $61,000 and $80,000. [3]
In the UK, entry-level positions offer around £18,000-£25,000, with mid-level salaries ranging from £25,000 to £35,000. Senior animators with over ten years’ experience can earn £40,000 or more. [4]
For senior with extensive experience and specialized knowledge, salaries can exceed these averages significantly. Such roles often require advanced skills and a deep understanding of animation techniques.
The growth prospects in the 2D animation industry are promising, with opportunities for advancement as animators gain experience and refine their skills. Earning potential grows alongside seniority and expertise.
Remember!
These are average figures. Actual salaries depend on your specific position, studio size, and current market conditions.
2D animation in 2023 and 2025

Right now, 2D animation is going through something of a revival. What makes it particularly interesting is how it’s bringing together classic techniques with modern technology. One of the biggest trends you’ll see is hybrid animation. Studios are mixing 2D and 3D elements in ways that open up new creative possibilities.
Software like Adobe Animate and Toon Boom Harmony have advanced significantly, making production faster and the final output higher quality. Animators can work more efficiently whilst still achieving the polished results audiences expect.
There’s another factor driving this resurgence: streaming platforms. Services like Netflix, Disney+, and others have created massive demand for 2D animated content.
Are there any real changes coming in 2026?
Looking at what’s happening in 2026, one thing is clear: animation has become more intentional. Instead of long, overbuilt formats, we’re seeing shorter, more precise pieces, designed with a clear understanding of where they’ll live and how they’ll be watched. This shift changes the way entire productions are planned, right from the start.
If you work with animation, or even just watch a lot of it, you’ve probably felt the fatigue caused by too many effects. More and more, the projects that stand out are calm, focused, and easy to follow. They guide the viewer step by step and tend to stay with you longer. Honestly, this direction resonates with us a lot.
AI is stepping into the process more visibly
You’ve likely noticed that AI comes up more and more in conversations about animation. In practice, though, its role is quite specific. It helps streamline repetitive tasks and makes it easier to test different versions of motion or editing. The creative decisions still belong to the animators.
This way of thinking is something we explore in more detail in our article Animations in generative AI results – are humans and algorithms playing on the same team? The strongest projects emerge when technology supports the process instead of dictating it. AI becomes a collaborator. Something like a smart intern who helps, but doesn’t take over.
Looking for a 2D animation studio that gets what you’re trying to achieve?
At Explain Visually, we’ve built our approach around understanding your project inside and out before we even start creating.
- Take a look at our portfolio (also on YouTube) to see the range of work we’ve delivered across different industries and styles. You’ll get a sense of how we approach visual storytelling and whether our creative direction aligns with what you have in mind.
- We’re transparent about pricing from the start. No hidden costs, no surprises halfway through. Just clear information so you can plan your budget confidently.
- We’ve handled projects of all sizes, from startups to established corporations.
- Check out our case studies to see how we’ve helped clients achieve measurable results, including one client who achieved a record 22,486% ROI.
If you’re serious about creating 2D animation that actually works for your business, let’s talk. We’ll walk you through how we can help.
𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐕𝐢𝐬𝐮𝐚𝐥𝐥𝐲 – 𝐁𝟐𝐁 𝐚𝐧𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐮𝐝𝐢𝐨:
- We create whiteboard animations for businesses
- We create corporate explainer videos
- We create visual storytelling for companies
Frequently Asked Questions about 2D Animation
How do animated videos differ from other visual formats?
Animated videos rely on illustrated motion rather than live footage, which gives creators more control over tone and style. Because animated visuals are built from scratch, they can simplify abstract topics without losing clarity.
Why are animation principles so important in 2D work?
Animation principles guide how movement feels on screen and help avoid stiff or unnatural motion. Even simple actions depend on timing, spacing, and rhythm to feel believable. Without them, animated commercials often look flat or rushed. Strong fundamentals shape the entire animation production process.
What skills matter most when starting in 2D animation?
A beginner needs solid drawing ability, but technical skills matter just as much over time. Learning how to adapt drawings for web animations teaches efficiency and consistency. Understanding the entire animation process also helps artists collaborate better with teams. Growth usually comes from practice.
How does classic animation style differ from modern workflows?
Classic animation style is rooted in traditional hand drawn techniques where every pose is created manually. Artists relied heavily on frame by frame animation to control timing and emotion. Modern tools automate parts of creating movement, but the artistic decisions remain similar. The difference lies more in speed than in intent.
What role does software play in fluid motion today?
Modern animation apps allow artists to reuse assets while still achieving fluid motion. This opens the door to various animation techniques that would have been impractical years ago. While computers help, the animator still decides how movement should feel.
Who oversees the creative direction of an animation project?
Animation directors are responsible for aligning visuals, pacing, and tone across the project. They translate complex ideas into a clear visual language that teams can follow. Their role becomes especially important when producing captivating animations at scale.
Why is 2D animation effective for explaining information?
2D animation breaks information down into clear visual elements that guide attention. Studios often use it to create visually stunning explanations without overwhelming the viewer. This approach works especially well for corporate videos where clarity matters more than spectacle.
What types of projects benefit most from 2D animation?
Brands frequently choose animated ads and animated explainer videos when they need flexible storytelling. The format works well for scalable animations that can be adapted across platforms. From social media to presentations, motion animation helps messages stay consistent. It also integrates easily with graphic design systems.
Source:
[1] ZipRecruiter Let’s Find Jobs for You: link: ZipRecruiter Ireland
[2] Talent.com “Animator: Average Salary in Canada, 2025”, link: animator Salary in Canada — Average Salary
[3] Ideed: 2D animator salary in Australia
Payscale, link: 2D Animation Salary in Australia | PayScale
[4] Indeed, link: 2D animator salary in United Kingdom
Prospects, link: Animator job profile |Prospects.ac.uk
Payscale, link: 2D Animation Salary in United Kingdom | PayScale