According to the Oxford Dictionary, the verb “animate” has two definitions: “To animate something or someone is to give (a film or character) the appearance of movement using animation techniques” and “To describe action as having the ability to come to life”.
Creating a “semblance of movement” involves creating a sequence of images—whether drawn, painted, or otherwise created by artistic means—that are slightly different from each other. Displayed in chronological order, these images create the illusion of changing shape and movement. What does the entire 2D animation process look like? What is the difference between Traditional Animation and Modern Animation and what kind of remuneration can specialists in this field expect?
Definition and history of 2D animation
2D animation is the art of creating movement within a two-dimensional space, encompassing characters, creatures, effects, and backgrounds. This medium achieves the illusion of movement by sequencing individual drawings over time. The origins of 2D animation date back to the late 19th century, with pioneers like Émile Reynaud and J. Stuart Blackton experimenting with sequential images to create motion, laying the groundwork for a revolutionary artistic medium.
Over time, 2D animation has evolved from hand-drawn frames to the use of digital technology, with modern tools like Toon Boom Harmony and Adobe After Effects enabling more efficient production while maintaining the medium’s timeless appeal.

In the world of 2D animation, animators work their magic by making characters, objects, and backgrounds move in a flat, two-dimensional environment. But it’s not just about drawing. These artists must also be great storytellers! Their job is to make sure that the way a character moves tells a clear story or message that keeps viewers on the edge of their seats from start to finish.

@ Copyright by Disney
Origins and evolution – history of animated films
In its early days, 2D animation was a painstaking process involving hand-drawn frames, with each second of animation typically divided into 24 frames.
Depending on the style, animators might use as many as 24 unique drawings per second (24fps) or as few as two, with the conventional approach, known as “on 2s”, involves creating a drawing every two frames (12fps) to save on production time and costs.
This traditional method has evolved significantly, with the advent of digital tools allowing for more complex and visually stunning animations (for example the implementation of digital techniques using computer software like Toon Boom Harmony or Adobe After Effects. ). The medium’s evolution has not only enhanced its visual capabilities but also expanded its applications across various platforms, from classic films like Disney’s “Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs” to modern digital content.
Timeless appeal and nostalgia
2D animation holds a cherished place in the hearts of all generations, evoking nostalgia and a sense of familiarity. Classic animations Disney’s remind us of the enduring charm of 2D animation.
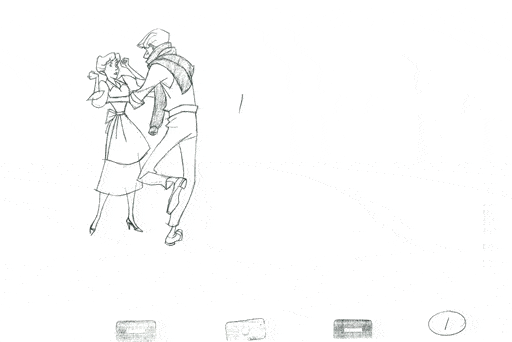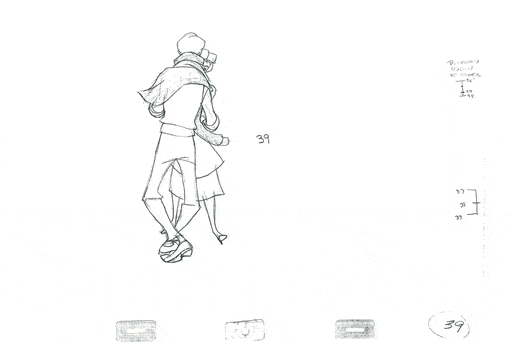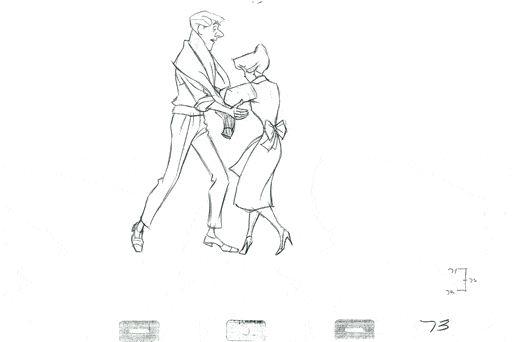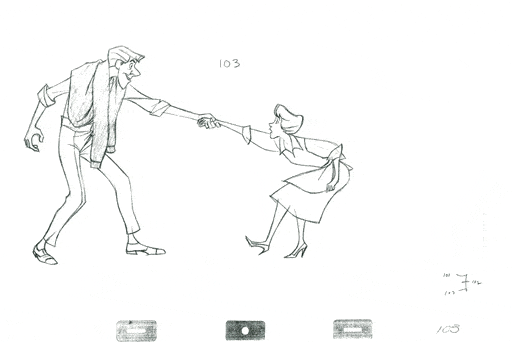
@ Copyright by Disney
Its versatility allows it to span multiple genres, from children’s tales to adult narratives, and its accessibility makes it an excellent entry point for aspiring animators. Despite technological advancements, 2D animation’s timeless appeal endures, offering a nostalgic and emotionally resonant experience.
2D animation today
2D animation is making a comeback and is more popular and diverse than ever! It can be found everywhere, from TV shows and video games to feature films, commercials, mobile apps and websites. Modern companies like Explain Visually and their hits like Vector animation for Mitsubishi Electric, Flobotics or Animation 2D for Opomarket are prime examples of its success. Even social media platforms like Snapchat are getting in on the action with brilliant 1-3 minute animated 2D episodes, and the gaming world is buzzing with 2D platformers like “Cuphead”.
You might not notice it right away, but animations are all around us on the Internet! From ads to entertainment, they play a huge role in enhancing our online experience.
He highlights the rapid evolution of the medium, with television animation booming and streaming services constantly on the hunt for new content.
These examples reflect the broad applications of 2D animation across various industries, from marketing and education to entertainment, highlighting its ability to engage audiences and convey messages effectively.
The demand for talented 2D animators has skyrocketed over the past decade. There’s a growing need for skilled artists who love motion graphics and can create original, engaging content that captivates audiences.
Visit our Explain Visually services page to learn how we help brands make their mark on the world with 2D animation.
Also check out: Animation vs. Illustration: Which is More Effective [Based on Research]
Types of 2D animation
Traditional animation (cel animation)

@ Copyright by Disney
Traditional animation, also known as hand-drawn or classical animation, is a time-honored animation technique where each frame is meticulously crafted by hand to create the illusion of motion. This process often involves drawing each frame on paper, which is then transferred onto transparent sheets known as cels. These cels are layered over static backgrounds to produce a complete scene.
Each frame captures incremental movements, which, when played in sequence, result in fluid motion. This painstaking process requires immense skill and patience, as animators must draw thousands of frames to complete a single animated feature.
Modern animation
In contrast to traditional methods, modern 2D animation leverages the power of computers to enhance and streamline the animation process. This digital approach allows animators to create characters, backgrounds, and animations using specialized software such as:
- Adobe Animate,
- Toon Boom Harmony,
- After Effects.
These programs offer tools that simplify the animation process, such as vector-based drawing, rigging systems, and motion tweening, which reduce the need for frame-by-frame drawing.
A fascinating fact about modern animation is its ability to integrate with other digital technologies, enabling the creation of interactive animations for video games, mobile apps, and websites. This evolution has expanded the scope of 2D animation, making it a versatile medium for various applications, from entertainment to education and marketing.
Interesting facts
Modern 2D animation software can simulate traditional techniques, allowing artists to create animations that retain the charm of hand-drawn work while benefiting from digital efficiency.
Read more: Animated ads – types, examples, prices.
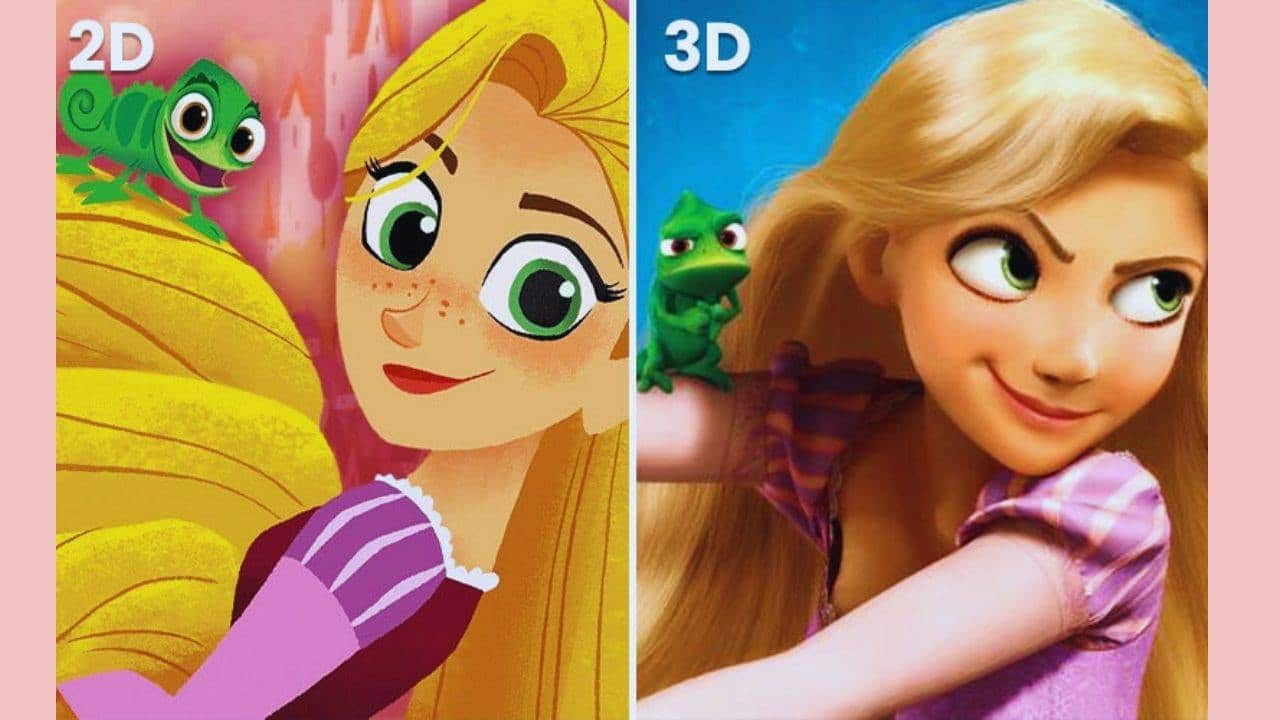
What is the difference between 2D and 3D animation?
2D and 3D animation are two distinct forms of animation that differ in several key aspects, including their visual style, production process, and applications.
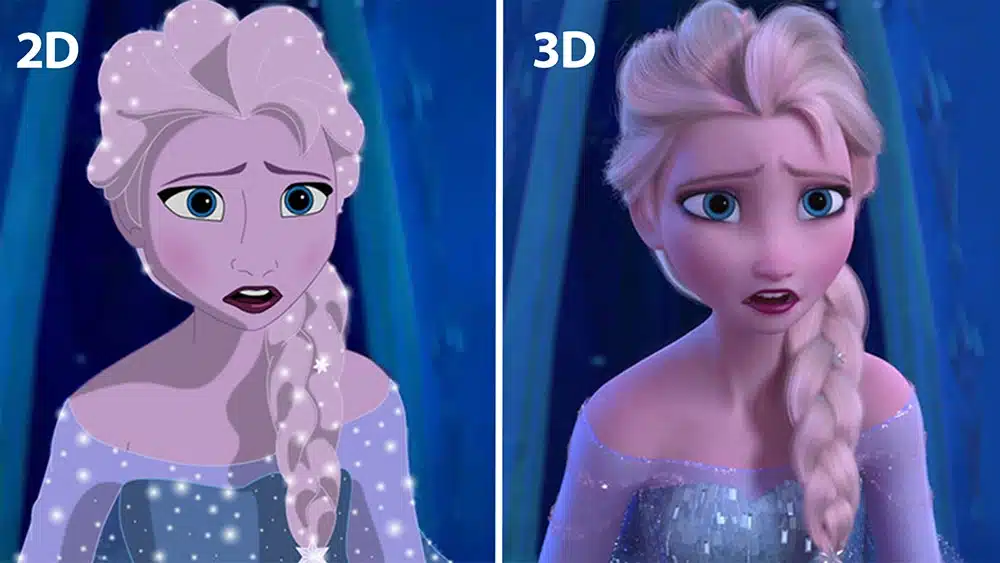
@ Copyright by Disney
Visual style
2D animation is a style that involves creating images in two dimensions, focusing on the X and Y axes. It usually has a flat appearance and is often more stylized and cartoonish. Characters and objects are drawn frame by frame, either by hand or using computer software.

@ Copyright by Disney
3D animation, on the other hand, involves creating images in three dimensions, adding depth (the Z axis) to the X and Y axes. This allows for more realistic and lifelike visualizations. 3D animation often involves modeling characters and environments in a 3D virtual space, providing a more immersive experience.
Production process
2D Animation generally involves drawing each frame individually, which can be less complex and quicker to produce.
3D Animation requires creating 3D models and rigging them for movement. This involves more complex software like Blender or Autodesk Maya and requires a deeper understanding of 3D modeling, texturing, and lighting. The process is more intricate and time-consuming, often involving a team of specialists.
Cost and time
2D Animation typically is more cost-effective and faster to produce than 3D animation. It requires less advanced technology and resources, making it a popular choice for projects with limited budgets.
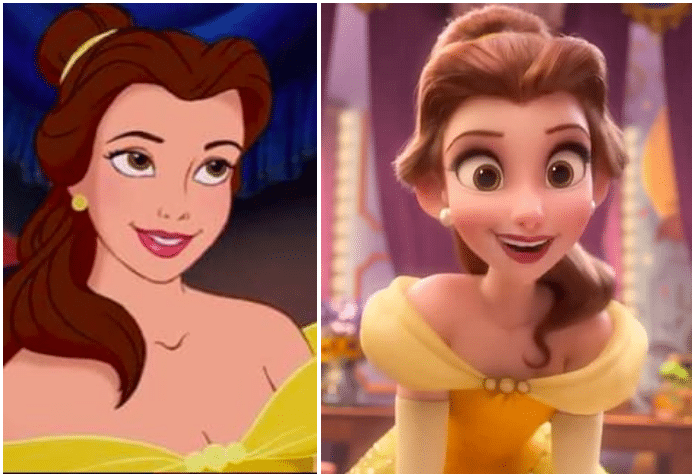
@ Copyright by Disney
3D Animation generally is more expensive and time-consuming due to the complexity of the production process. It requires powerful computers and specialized software, which can increase costs significantly (computer animation).
Read more: Price of an explainer video – how much does it cost and why?
The animation process
Let’s break down the production process of 2D animation. It should be noted that every animated film is produced differently, utilizing various techniques and technologies. But remember…
There is no singular “right” way to animate, and the steps described may be executed in different orders. What we present here is a widely practiced method in prominent animation studios like Disney, Dreamworks, and Ghibli.
The process of creating 2D animation is segmented into three distinct parts:
- pre-production;
- production;
- post-production.
These stages include multiple sub-stages that are integral to building a comprehensive animated work.
2D pre-production stage – scripting and storyboarding
The pre-production stage includes finding inspiration, developing an idea, finalizing the script, and scheduling the production.
This stage consists of different mini-stages that are the building blocks of a complete animated work.
2D production stage – design and animation
In the production stage, the process includes designing and optionally:
- composing theme songs,
- storyboarding,
- developing concept art,
- recording voices,
- animating,
- applying ink and color.

@ Copyright by Disney
Each of these processes contains several sub-stages, which are crucial to constructing a complete animated piece.
Post-production stage – sound design and editing
The post-production stage of animation is a crucial phase where sound design and editing come together to enhance the final product.
- Sound design and effects.
- Recording and editing dialogue.
- Sound mixing and final assembly.
- Visual effects integration.

@ Copyright by Disney
The post-production stage is where all the elements of the animation come together, transforming separate components into a polished and cohesive final product. This phase requires close collaboration between sound designers, editors, and directors to ensure that the audio and visual elements work harmoniously to deliver the intended artistic vision.
Artistic and technical skills for 2D animation
2D animators must possess a strong foundation in drawing and illustration, as these skills are essential for creating expressive characters and dynamic scenes. They need to understand the principles of animation, such as timing, spacing, and squash and stretch, to bring characters and stories to life in a believable manner. Technical proficiency with 2D animation software, such as Adobe Animate or Toon Boom Harmony, is crucial for executing animations efficiently and effectively.
Additionally, animators should have a keen eye for detail and composition, enabling them to craft visually appealing and coherent scenes. Experience with storyboarding and character design can further enhance an animator’s ability to contribute creatively to a project, ensuring that the animation aligns with the overall narrative and artistic vision.
Career opportunities and salary expectations in 2D animation – job roles and industries
2D animators can find work in a diverse range of industries, including feature films, television shows, video games, and advertising. Within these sectors, animators may be employed by production companies, animation studios, or advertising agencies to create content for commercials, mobile apps, and websites.
The roles available in these industries are varied, ranging from animators and storyboard artists to character designers and background painters. As technology evolves, new roles continue to emerge, offering fresh opportunities for those entering the field.
Salary ranges and growth prospects
The salary expectations for 2D animators vary widely based on factors such as experience, location, and industry.
- For entry-level positions, the average salary in the United States is approximately USD $43,000 per year. As animators gain experience and move into mid-level roles, the average salary increases to around USD $74,000. These figures can fluctuate depending on the specific industry and geographic location.
- In Canada, entry-level animators can expect to earn between CAD $35,000 and $50,000, while mid-level positions offer salaries ranging from CAD $59,000 to $77,000.
- In Australia and New Zealand, entry-level salaries start at AUD $48,000, with mid-level roles commanding between AUD $50,000 and $95,000.
- In the UK, entry-level positions offer around GBP £24,270, with mid-level salaries ranging from GBP £36,000 to £47,500.
For senior, animation director or technical animators with extensive experience and specialized knowledge, salaries can exceed these averages significantly. Such roles often require advanced skills and a deep understanding of animation techniques, which can lead to higher compensation packages.
Overall, the growth prospects in the 2D animation industry are promising, with opportunities for advancement as animators gain experience and refine their skills. The potential for higher earnings increases with seniority and expertise, making it a rewarding career path for those dedicated to honing their craft. Note that these salary figures are averages and can vary considerably based on the specific role and market conditions.
Sources: prospects.ac.uk; adzuna.co.uk; cwjobs.co.uk; LinkedIn; instantoffices.com
2D animation in 2023 and 2024
In 2023 and 2024, 2D animation is experiencing a renaissance, as it combines time-honored techniques with state-of-the-art technology. The trend of hybrid animations, which blend 2D and 3D components, is expanding creative horizons. Advanced tools like Adobe Animate and Toon Boom Harmony are now more capable than ever, facilitating efficient production processes and superior quality.
Additionally, the booming popularity of streaming services has led to an increased appetite for 2D animated content, marking an exciting era for animators and viewers alike.
2D animation with Explain Visually
Are you in search of a 2D animation studio? It’s important to carefully evaluate several key factors to ensure you select the right partner for your project.
- Examine the studio’s portfolio to get a sense of their style, quality, and range of work. This will help you determine if their artistic vision aligns with your project goals.
- Consider their pricing structure to ensure it fits within your budget. Transparent pricing can help avoid unexpected costs down the line.
- Assess the studio’s capacity and ability to handle your project’s scope and timeline. A studio with adequate resources and a proven track record of managing similar projects can provide reassurance of timely delivery.
- Evaluate their project volume and workload to ensure they can dedicate sufficient attention to your project.
By thoroughly considering these aspects, you can choose a 2D animation studio that best meets your specific needs and expectations.