Introduction: The Role of Animation in Contemporary Communication and Its Relevance in IT
Animation has evolved significantly from its roots in entertainment to become a crucial tool in contemporary communication, especially within the information technology (IT) sector. Today, animation is widely recognized for its ability to convey complex ideas through dynamic and engaging visual storytelling. This characteristic is particularly valuable in IT, where explaining complex systems and technologies clearly and effectively can be challenging.
Animation aids in simplifying dense technical content, such as network operations, software functionality, and data management. By visually representing these concepts, animation makes them more accessible and easier to understand for non-specialists. For instance, an animated explainer video can show how a particular software operates or what cloud computing is, which helps bridge the knowledge gap for general audiences.
Furthermore, the integration of animation in digital communications not only enhances understanding but also improves user experience by making interactions with digital products more intuitive and engaging. As technology advances, the role of animation in the IT sector is expanding, offering innovative ways to visualize and interact with data and processes that are crucial for tech industry stakeholders.
This transition underscores the shifting role of animation from pure entertainment to a vital educational and communicative tool in one of the most technically complex industries today.
I. Historical Context: Evolution of Animation from Entertainment to a Business Tool
The journey of animation from a form of entertainment to an invaluable business and educational tool encompasses a century of innovation and technological advancement. Initially emerging as an artistic medium in the early 20th century, animation quickly became a popular form of entertainment with the creation of iconic characters like Felix the Cat in 1919 and Mickey Mouse in the late 1920s.The first significant shift towards animation’s educational potential occurred with the advent of rotoscoping by Max Fleischer in 1915. This technique allowed for more realistic animations by tracing over live-action film, making animated content more relatable and easier to understand for educational purposes.
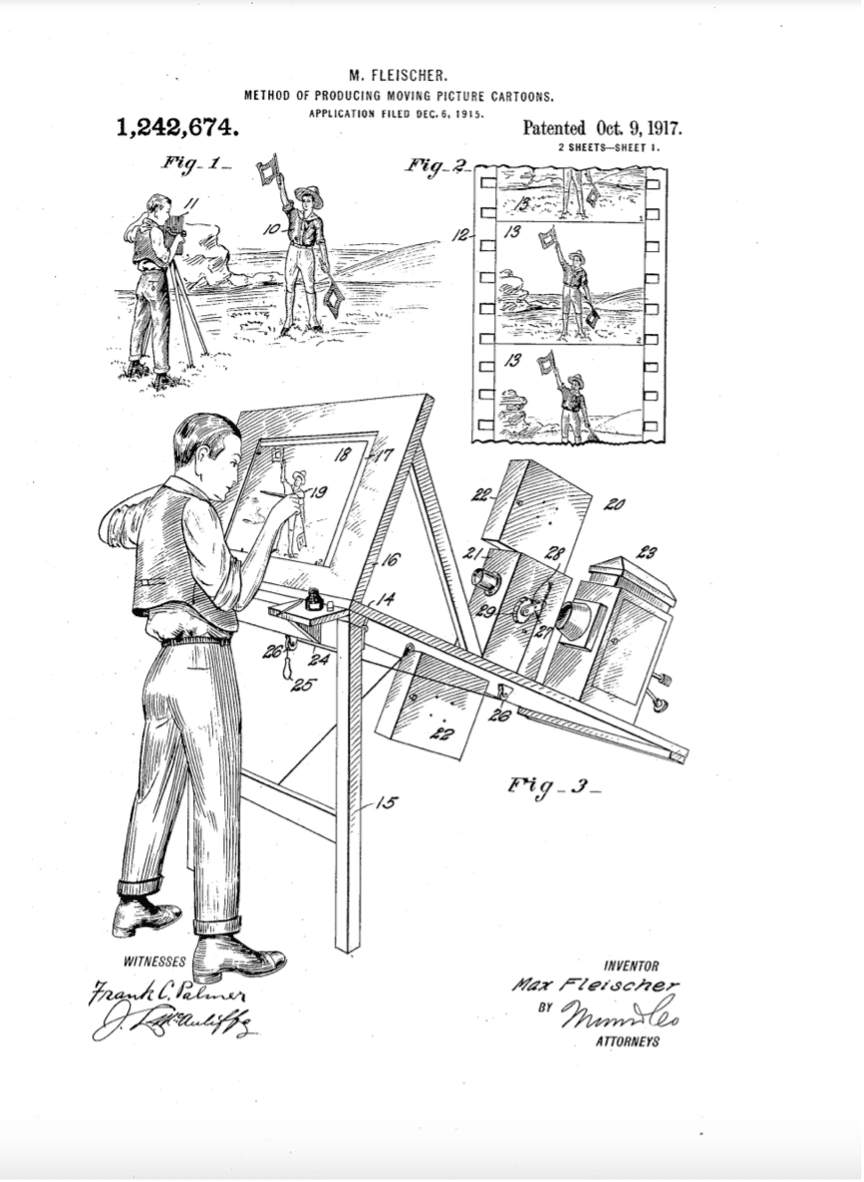
[Image source: United States Patent Office]
As technology progressed, the introduction of computer-generated imagery (CGI) in the 1980s and 1990s revolutionized animation, transitioning it from traditional hand-drawn methods to sophisticated digital techniques. This period marked a turning point where animation began to be seen not just as entertainment but as a tool in visual communication, capable of illustrating complex processes in fields such as science, medicine, and engineering.
In business and education, the 1990s onward saw a significant adoption of animation due to the rise of personal computers and the internet. Animation became a preferred medium for corporate training, educational content, and digital marketing. Companies utilized animation for everything from employee training and safety videos to customer service explanations and product demonstrations, appreciating its ability to capture complex details in an engaging, memorable manner.
Today, animation is entrenched in the educational technology landscape, enhancing learning experiences by making abstract concepts concrete and simplifying complex information. It supports various educational activities, including interactive learning modules and online courses, where it helps maintain student engagement and enhances understanding.
The evolution of animation showcases its versatility and enduring appeal, affirming its role as a critical tool in both business and educational contexts. Its ability to adapt and grow with technological advancements continues to make it a valuable asset for complex communication and learning strategies.
II. The Need for Animation in IT
Information Technology (IT) encompasses complex concepts such as cloud computing, machine learning algorithms, and cybersecurity protocols. These subjects involve abstract and complicated processes that are often challenging to grasp, especially for those without a background in technology. For example, visualizing how data travels across networks or how encryption secures information requires more than static diagrams or textual descriptions.
Communicating these complex IT concepts to non-experts – such as stakeholders, clients, or entry-level employees – presents significant challenges. Traditional methods like lengthy documents or standard presentations can fail to capture and retain the audience’s attention effectively. Moreover, without a proper understanding, these audiences could take less informed decisions that impact the business negatively.
This is where animation plays a crucial role. Animated content can transform highly complex IT concepts into engaging, understandable visual narratives. For instance, an animated video can effectively illustrate how a cybersecurity attack happens and the subsequent response steps, making the information accessible to everyone, not just IT professionals.
Statistical Insights:
The growing recognition of animation’s effectiveness is reflected in industry statistics:
- Market Growth: The global animation market is developing rapidly, with forecasts indicating that it could reach a value of around 400 billion dollars by 2023, which indeed has proven to be accurate, highlighting the growing investments in animation for various applications, including information technology. According to Global Newswire and Precedence Research, the market value was approximately 394.6 billion dollars in 2022 and around 412.96 billion dollars in 2023, reflecting an annual growth rate of about 5%.
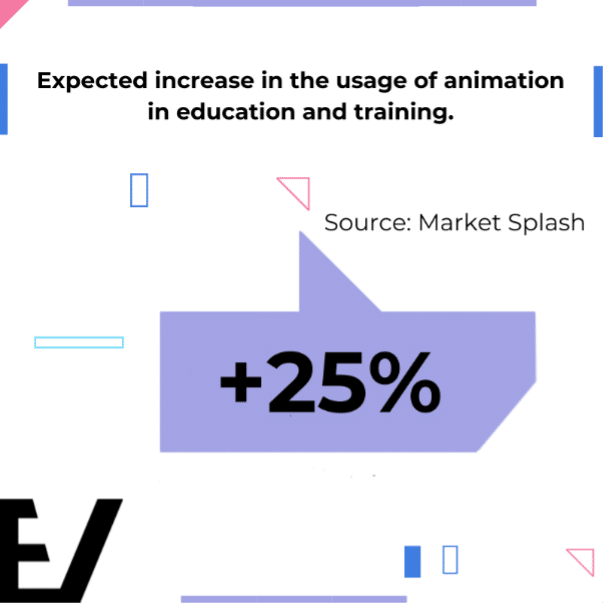
- Education and Training: Specifically, the use of animation in education and training is expected to grow by 40% annually. This statistic underscores the value of animation in creating engaging learning experiences, which is essential for training purposes in IT, where new software and technologies are constantly being introduced.
- Technological Adoption: The adoption of animation in technology-driven sectors like virtual and augmented reality is also on the rise, expected to increase by 20% annually. In IT, this could mean more immersive and interactive training modules or simulations designed to give a real-world feel of IT environments through animation.
III. Benefits of using animation in IT
Animation offers significant benefits in the IT sector, particularly in explaining complex concepts, increasing engagement and retention, and depicting dynamic processes effectively. It takes abstract IT topics and turns them into comprehensible videos, making challenging concepts like software architecture or network systems accessible and understandable. This is particularly useful in educational contexts, and in professional environments where stakeholders need clear insights into technological functionalities to make the right decisions.
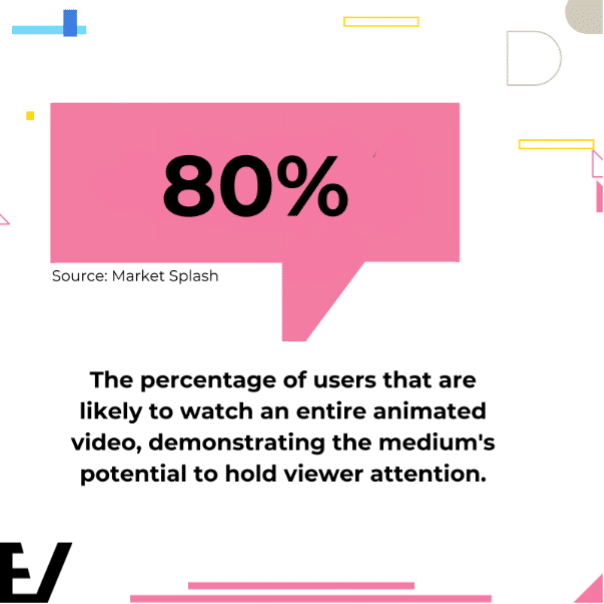
Furthermore, animations are more engaging and help users retain information more effectively. Studies suggest that animated content can significantly improve learning outcomes by making the viewing experience more engaging and memorable. This is confirmed by statistics indicating that 80% of users are likely to watch an entire animated video, demonstrating the medium’s potential to hold viewer attention.
Animations are also invaluable for illustrating IT processes that are dynamic by nature, such as data flows or the functioning of algorithms in real-time. They can visually simulate scenarios that are otherwise difficult to explain, such as cybersecurity attacks or data encryption, providing viewers with a step-by-step understanding of complex processes.
The increasing application of animation in educational and professional settings in IT is reflected in the growing market value, with the educational animation sector alone valued at about $3 billion and expected to grow significantly. This underscores the expanding role of animation not just in media and entertainment but in sectors demanding high levels of precision and clarity in communication.
Overall, the use of animation in IT not only simplifies the delivery of complex information but also enhances learner engagement and aids in the detailed illustration of technical processes, proving to be an indispensable tool in the digital age.
IV. Case Studies: The Impact of Animation in IT
DROPBOX
Dropbox utilized an animated explainer video to convey how their service works in a simple and engaging way. This approach was crucial in helping them to stand out in a competitive market and contributed significantly to their rapid growth. The video helped Dropbox acquire 10 million global customers, demonstrating the power of effective visual storytelling in simplifying complex IT solutions and driving substantial user engagement and conversion.
KASPERSKY LAB
Kaspersky Lab, a leader in cybersecurity, leveraged an animated explainer video to break down their complex cybersecurity tools into understandable segments. This not only educated potential users about their new personal security platform but also increased the excitement and energy around the product pre-launch. The result was a 300% boost in website traffic and a significant increase in customer acquisitions, illustrating the effectiveness of animation in clarifying IT products and enhancing market reach.
VARPET
Varpet’s use of an animated explainer video for their service, which connects users with reliable help for household chores, resulted in 15,000 app registrations in just one month and a 200% improvement in conversion rate. The animation helped convey the ease and efficiency of their service, engaging users and simplifying the process of finding help, which can often be daunting and tedious.
These examples underscore the transformative impact that animation can have in the IT sector. Animated videos not only enhance the clarity and appeal of complex IT solutions but also significantly improve user engagement and conversion rates, proving to be a powerful tool for communication and marketing in the tech industry. For more details, you can explore these case studies and others at sources like Yans Media and Creative Island Studio.
V. Creating Effective IT Animations
Best Practices in Scriptwriting, Storyboard Creation, and Technical Accuracy
- Scriptwriting:
- Understand Your Audience: Begin by understanding who the animation is for. Knowing whether the audience is experienced in the tech sector, or has no previous experience can drastically change the language, terminology, and complexity used.
- Define the Core Message: Keep the core message focused. In IT, whether explaining a product or a concept, it’s crucial to define what the key takeaway for the audience should be.
- Use Relatable Scenarios: Incorporate scenarios or problems that the target audience might face, which the IT solution can resolve. This not only makes the animation relatable but also demonstrates the utility of the IT solution in real-world applications.
- Storyboard Creation:
- Visual Planning: Storyboarding is essential for planning out the animation visually. This step helps in mapping out the flow of the narrative, ensuring a logical progression that builds understanding step-by-step.
- Feedback Loops: Integrate feedback loops into the storyboard creation phase. Showing the storyboard to a test audience or stakeholders can provide insights into whether the content is hitting the mark or if adjustments are needed.
- Technical Accuracy:
- Consult IT Experts: Throughout the scripting and storyboarding process, regularly consult IT experts to ensure that all technical details are correct. Misrepresenting technical information can damage credibility and confuse the audience.
- Simplify without Oversimplifying: Strike a balance between simplification and accuracy. The goal is to make the content accessible without stripping away the essence of the technology.
The Role of Collaboration Between IT Professionals and Creative Teams:
- Integration of Expertise:
- Successful IT animations often result from the seamless integration of expertise from both IT professionals and creative teams. IT experts provide the technical content and understanding, while creatives translate this into engaging and understandable visual stories.
- Communication is the Key:
- Maintain open and ongoing communication between the IT professionals and the creative team. This ensures that the animations remain technically accurate while being effectively communicated.
- Use regular meetings and shared tools to keep everyone aligned on the project goals, updates, and feedback.
- Iterative Process:
- Treat the development of IT animations as an iterative process. Initial drafts should be reviewed by both IT and creative sides to refine the technical content and the narrative delivery.
- Iterations help refine the animation, making it more engaging and clearer with each version.
Creating effective IT animations involves a careful blend of technical accuracy, creative storytelling, and collaborative effort. By adhering to these practices, IT animations can significantly enhance understanding and engagement with complex technical content, making them invaluable tools for education, marketing, and user support within the tech industry.
VI. Future Trends in Animation Technologies for IT
Predictions About the Development of Animation Technologies
- Increased Integration of AI and Machine Learning:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are expected to play a significant role in automating parts of the animation process, such as lip-syncing, facial expressions, and even complex animation sequences. This will not only speed up the production process but also enhance the customization capabilities of animations, making them more adaptable to user interactions in real-time.
- Advancements in Real-Time Animation:
- Developments in real-time rendering technologies will likely continue, driven by advancements in gaming and virtual reality. For IT, this means animations can be generated on-the-fly based on user input, allowing for more interactive and personalized educational or troubleshooting tools.
- Greater Adoption of AR and VR:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) will increasingly be used to create more immersive learning and operational environments in IT. These technologies can simulate real-world IT scenarios, providing hands-on experience in a controlled, virtual space.
Emerging Tools and Platforms That Could Enhance Animation’s Effectiveness in IT
- Cloud-Based Animation Tools:
- Cloud platforms are expected to become more prevalent for animation creation, offering high-performance rendering without the need for expensive local hardware. Cloud-based tools can also facilitate collaboration across different geographies in real-time, which is crucial for global IT teams.
- Advanced Motion Capture Systems:
- As motion capture technology becomes more refined and accessible, it will allow for more nuanced and precise animations. This can be particularly beneficial for creating training modules in IT that require detailed demonstrations of physical tasks, such as managing hardware or performing manual repairs.
- Interactive Animation Platforms:
- New platforms are emerging that enable users to interact with animations. For instance, platforms might allow IT students or professionals to manipulate animated models of network setups or data flows, enhancing their understanding through direct interaction.
- Enhanced 3D Visualization Tools:
- Tools that offer sophisticated 3D visualization capabilities will become more integrated into IT systems, helping to model complex data structures and systems architectures visually and intuitively. These tools will help demystify advanced concepts such as big data analytics and cloud computing architectures.
These trends and tools represent just a glimpse of what the future holds for animation in IT. As technology evolves, so too will the ways in which animations are created and utilized, driving greater efficiency and deeper understanding in complex technical fields.
VII. Conclusion: The Transformative Role of Animation in IT Communications
Animation has emerged as a pivotal tool in conveying complex IT concepts, enhancing user engagement, and illustrating dynamic processes within the IT industry. By transforming abstract ideas into visually engaging narratives, animation serves not only to educate but also to facilitate a deeper understanding and retention of technical information.
Key Points Recap:
- Visualization: Animation excels in making intricate IT concepts accessible and understandable through dynamic visual representation.
- Engagement and Retention: Animated content captures attention more effectively than static images or text, significantly enhancing information retention and user engagement.
- Dynamic Illustration: Animation is uniquely suited to depict the continuous and interactive processes characteristic of IT systems, providing clear visualizations of data flows and software interactions.
Future Trends:
The future of animation in IT looks promising with advancements in AI, real-time animation, and immersive technologies like AR and VR. These innovations will further refine the effectiveness of animations, making them more interactive and personalized to user needs.
Long-term Impact:
As IT systems continue to evolve in complexity, animation will play an increasingly critical role in education, troubleshooting, and marketing within the sector. The ability to simplify and visually communicate complex data and processes will remain invaluable, potentially revolutionizing how IT education and professional training are conducted.
Explain Visually specializes in creating tailored IT animations that bridge the gap between complex IT solutions and user comprehension. For more information on how our expertly crafted animations can enhance your IT communications and training needs, contact us!
This focus on specialized IT animations underscores our commitment to enhancing understanding and interaction through innovative visual solutions, preparing businesses and professionals for the technological challenges of the future.